Supracondylar humerus fracture
| Supracondylar humerus fracture | |
|---|---|
 |
|
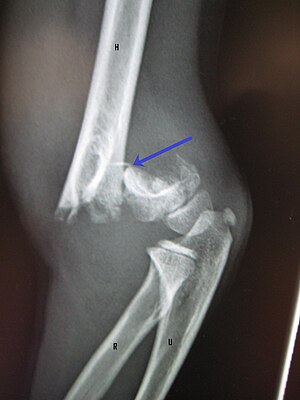
| An elbow X-ray showing a displaced supracondylar fracture in a young child |
| Classification |
· ·
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
A supracondylar humerus fracture is a fracture of the distal humerus just above the elbow joint. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. In children, many of these fractures are non-displaced and can be treated with casting. Some are angulated or displaced and are best treated with surgery. In children, most of these fractures can be treated effectively with expectation for full recovery. Some of these injuries can be complicated by poor healing or by associated blood vessel or nerve injuries with serious complications.
Extension type of supracondylar humerus fractures typically result from a fall on to an outstretched hand, usually leading to a forced hyperextension of the elbow. The olecranon acts as a fulcrum which focuses the stress on distal humerus (supracondylar area), predisposing the distal humerus to fracture. The supracondylar area undergoes remodeling at the age of 6 to 7, making this area thin and prone to fractures. Important arteries and nerves (brachial artery, median nerve, radial nerve, and ulnar nerve) are located at the supracondylar area and can give rise to complications if these structures are injured. Meanwhile, the flexion-type of supracondylar humerus fracture is less common. It occurs by falling on the point of the elbow, or falling with the arm twisted behind the back. This causes anterior dislocation of the proximal fragment of the humerus.
A child will complain of pain and swelling over the elbow immediately post trauma with loss of function of affected upper limb. Late onset of pain (hours after injury) could be due to muscle ischaemia (reduced oxygen supply). This can lead to loss of muscle function.
It is important to check for viability of the affected limb post trauma. Clinical parameters such as temperature of the limb extremities (warm or cold), capillary refilling time, oxygen saturation of the affected limb, presence of distal pulses (radial and ulnar pulses), assessment of peripheral nerves (radial, median, and ulnar nerves), and any wounds which would indicate open fracture. Doppler ultrasonography should be performed to ascertain blood flow of the affected limb if the distal pulses are not palpable. Anterior interosseus branch of the median nerve most often injured in postero-lateral displacement of the distal humerus as the proximal fragment is displace antero-medially. This is evidenced by the weakness of the hand with a weak "OK" sign on physical examination (Unable to do an "OK" sign; instead a pincer grasp is performed). Radial nerve would be injured if the distal humerus is displaced postero-medially. This is because the proximal fragment will be displaced antero-laterally. Ulnar nerve is most commonly injured in the flexion type of injury because it crosses the elbow below the medial epidcondyle of the humerus.
...
Wikipedia
