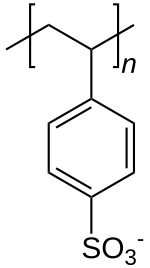
Sulfonated polystyrene
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names |
Sodium salt: Kayexalate, Kionex, Resonium A Calcium salt: Calcium Resonium, Sorbisterit, Resikali |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682108 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral, retention enema |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | None |
| Metabolism | None |
| Excretion | Faeces (100%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| KEGG | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.167.553 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | [C8H7SO3−]n |
|
|
|
Polystyrene sulfonates are polymers derived from polystyrene by the addition of sulfonate functional groups. They are widely used as ion-exchange resins to remove ions such as potassium, calcium, and sodium from solutions in technical or medical applications.
Linear ionic polymers are generally water-soluble, whereas cross-linked materials (called resins) do not dissolve in water. These polymers are classified as polysalts and ionomers.
Polystyrene sulfonate is usually supplied in either the sodium or calcium form. It is used as a potassium binder in acute and chronic kidney disease for people with hyperkalemia (abnormal high blood serum potassium levels). However, it is unclear if it is medically beneficial and there is concern about possible side effects when it is combined with sorbitol.
Polystyrene sulfonates are given by mouth with a meal or rectally by retention enema.
Under the name tolevamer, a polystyrene sulfonate was investigated by Genzyme as a toxin binding agent for the treatment of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhoea (CDAD), but it was never marketed.
The drug is contraindicated in patients with obstructive bowel disease and in newborn children with reduced gut motility.
...
Wikipedia
