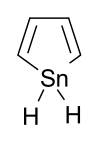
Stannole
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
1H-Stannole
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C4H6Sn | |||
| Molar mass | 172.80 g·mol−1 | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Stannole is an organotin compound with the formula (CH)4SnH2. It is classified as a metallole, i.e. an unsaturated five-membered ring containing a heteroatom. It is a structural analog of pyrrole, with tin replacing the nitrogen. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, are also called stannoles.
1,1-Dibutylstannole is a pale yellow oil prepared from 1,4-dilithio-1,3-butadiene and dibutyltin dichloride
1,1-Dimethyl-2,3,4,5-tetraphenyl-1H-stannole, for example, can be formed by the reaction of 1,4-dilithio-1,2,3,4-tetraphenyl-1,3-butadiene and dimethyltin dichloride. 1,1-Disubstituted stannoles can be formed in the [2+2+1] cycloaddition reaction of two acetylene molecules with an organotin molecule SnR2.
...
Wikipedia