Splenius capitis muscle
| Splenius capitis muscle | |
|---|---|

Muscles connecting the upper extremity to the vertebral column (splenius capitis et cervicis labeled at upper right).
|
|
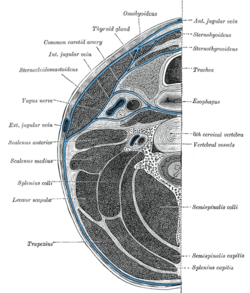
Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the deep cervical fascia (splenius capitis labeled at bottom right).
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | Nuchal ligament and spinous process of C7-T3 |
| Insertion | Mastoid process of temporal and occipital bone |
| Artery | Muscular branches of the aorta |
| Nerve | Posterior ramus of spinal nerves C3 and C4 |
| Actions | Extend, rotate, and laterally flex the head |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus splenius capitis |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
m_22/12550912 |
| TA | A04.3.02.103 |
| FMA | 22653 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
The splenius capitis (/ˈspliːni.əs ˈkæpᵻtᵻs/) (from Greek spléníon, meaning 'bandage', and Latin caput, meaning 'head') is a broad, straplike muscle in the back of the neck. It pulls on the base of the skull from the vertebrae in the neck and upper thorax. It is involved in movements such as shaking the head.
It arises from the lower half of the nuchal ligament, from the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra, and from the spinous processes of the upper three or four thoracic vertebrae.
The fibers of the muscle are directed upward and laterally and are inserted, under cover of the sternocleidomastoideus, into the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and into the rough surface on the occipital bone just below the lateral third of the superior nuchal line. The splenius capitis is deep to sternocleidomastoideus at the mastoid process, and to the trapezius for its lower portion. It is one of the muscles that forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck.
...
Wikipedia
