Sore Throat
| Sore throat | |
|---|---|
 |
|
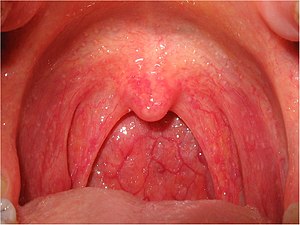
| Viral pharyngitis, the most common cause of a sore throat. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Otorhinolaryngology |
| ICD-10 | J02, J31.2 |
| ICD-9-CM | 472.1 |
| DiseasesDB | 24580 |
| MedlinePlus | 000655 |
| eMedicine | emerg/419 |
| MeSH | D010612 |
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat.
It is usually caused by pharyngitis (inflammation of the throat) or tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils). It can also result from trauma.
About 7.5% of people have a sore throat in any three-month period.
A sore throat is pain anywhere in the throat.
A sore throat is usually from irritation or inflammation. The most common cause (80%) is acute viral pharyngitis, a viral infection of the throat. Other causes include other infections (such as ), trauma, and tumors.Gastroesophageal (acid) reflux disease can cause stomach acid to back up into the throat and also cause the throat to become sore. In children streptococcal pharyngitis is the cause of 37% of sore throats.
Analgesics such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and paracetamol (acetaminophen) help in the management of pain. The Mayo Clinic advises gargling with salty warm water and resting the voice. Symptoms without active treatment usually last two to seven days.
In the United States there are about 2.4 million emergency department visits with throat-related complaints per year.
...
Wikipedia
