Somatopleure
| Somatopleuric mesenchyme | |
|---|---|

A series of a transverse sections through an embryo of the dog. (After Bonnet.) Section I is the most anterior. In V the neural plate is spread out nearly flat. The series shows the uprising of the neural folds to form the neural canal. a. Aortæ. c. Intermediate cell mass. ect. Ectoderm. ent. Entoderm. h, h. Rudiments of endothelial heart tubes. In III, IV, and V the scattered cells represented between the entoderm and splanchnic layer of mesoderm are the vasoformative cells which give origin in front, according to Bonnet, to the heart tubes, h; l.p. Lateral plate still undivided in I, II, and III; in IV and V split into somatic (sm) and splanchnic (sp) layers of mesoderm. mes. Mesoderm. p. Pericardium. so. Primitive segment.
|
|
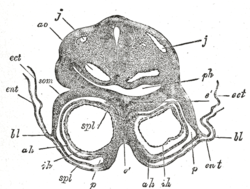
Transverse section through the region of the heart in a rabbit embryo of nine days. X 80. (Kölliker.) j, j. Jugular veins. ao. Aorta. ph. Pharynx. som. Somatopleure. bl. Proamnion. ect. Ectoderm. ent. Entoderm. p. Pericardium. spl. Splanchnopleure. ah. Outer wall of heart. ih. Endothelial lining of heart. é. Septum between heart tubes.
|
|
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 9 |
| Precursor | lateral plate mesoderm, ectoderm |
| Gives rise to | mesenchyme |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | mesenchyma somatopleurale |
| Code | TE E4.0.4.1.0.0.3 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
In the anatomy of an embryo, the somatopleuric mesenchyme is a structure created during embryogenesis when the lateral mesoderm splits into two layers. The outer (or somatic) layer becomes applied to the inner surface of the ectoderm, and with it forms the somatopleure.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
...
Wikipedia
