Solutrean
 |
|
| Geographical range | Western Europe |
|---|---|
| Period | Epipaleolithic |
| Dates | c. 22,000 – c. 17,000 BP |
| Type site | Parc archéologique et botanique de Solutré |
| Preceded by | Gravettian |
| Followed by | Magdalenian |
| The Paleolithic |
|---|
|
↑ Pliocene (before Homo) |
|
Lower Paleolithic (c. 3.3 Ma – 300 ka)
(300–45 ka)
(50–10 ka)
|
| ↓ Mesolithic ↓ Stone Age |
↑ Pliocene (before Homo)
The Solutrean industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Palaeolithic, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP.
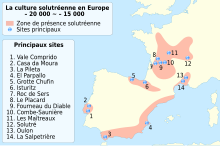
The term Solutrean comes from the type-site of "Cros du Charnier," dating to around 21,000 years ago and located at Solutré, in east-central France near Mâcon. The Rock of Solutré site was discovered in 1866 by the French geologist and paleontologist Henry Testot-Ferry. It is now preserved as the Parc archéologique et botanique de Solutré.
The industry was named by Gabriel de Mortillet to describe the second stage of his system of cave chronology, following the Mousterian, and he considered it synchronous with the third division of the Quaternary period. The era's finds include tools, ornamental beads, and bone pins as well as prehistoric art.
Solutrean tool-making employed techniques not seen before and not rediscovered for millennia. The Solutrean has relatively finely worked, bifacial points made with lithic reduction percussion and pressure flaking rather than cruder flintknapping. Knapping was done using antler batons, hardwood batons and soft stone hammers. This method permitted the working of delicate slivers of flint to make light projectiles and even elaborate barbed and tanged arrowheads. Large thin spearheads; scrapers with edge not on the side but on the end; flint knives and saws, but all still chipped, not ground or polished; long spear-points, with tang and shoulder on one side only, are also characteristic implements of this industry. Bone and antler were used as well.
...
Wikipedia
