Sodium pump
| Na+/K+ ATPase pump | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
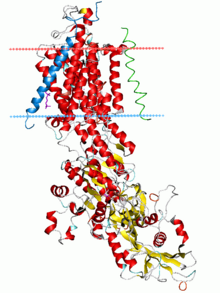
Sodium-potassium pump, E2-Pi state. Calculated hydrocarbon boundaries of the lipid bilayer are shown as blue (intracellular) and red (extracellular) planes
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.6.3.9 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
Na+
/K+
-ATPase (sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, also known as the Na+
/K+
pump or sodium–potassium pump) is an enzyme (an electrogenic transmembrane ATPase) found in the plasma membrane of all animal cells. It performs several functions in cell physiology.
The Na+
/K+
-ATPase enzyme is a solute pump that pumps sodium out of cells while pumping potassium into cells, both against their concentration gradients. This pumping is active (i.e. it uses energy from ATP). For every ATP molecule that the pump uses, three sodium ions are exported and two potassium ions are imported; there is hence a net export of a single positive charge per pump cycle.
...
Wikipedia
