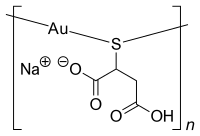
Sodium aurothiomalate
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Myocrisin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intramuscular |
| ATC code | M01CB01 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | High |
| Biological half-life | 6-25 days |
| Excretion | Urine (60-90%), faeces (10-40%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | 12244-57-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 16760302 |
| ChemSpider |
7827788 |
| UNII |
E4768ZY6GM |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:35863 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C4H4AuNaO4S |
| Molar mass | 367.939350590 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Sodium aurothiomalate (INN, known in the United States as gold sodium thiomalate) is a gold compound that is used for its immunosuppressive anti-rheumatic effects. Along with an orally-administered gold salt, auranofin, it is one of only two gold compounds currently employed in modern medicine.
It is primarily given once or twice weekly by intramuscular injection for moderate-severe rheumatoid arthritis although it has also proven itself effective in treating tuberculosis.
Its most common side effects are digestive (mostly dyspepsia, mouth swelling, nausea, vomiting and taste disturbance), vasomotor (mostly flushing, fainting, dizziness, sweating, weakness, palpitations, shortness of breath and blurred vision) or dermatologic (usually itchiness, rash, local irritation near to the injection site and hair loss) in nature, although conjunctivitis, blood dyscrasias, kidney damage, joint pain, muscle aches/pains and liver dysfunction are also common. Less commonly, it can cause GI bleeds, dry mucous membranes and gingivitis. Rarely it can cause: aplastic anaemia, ulcerative enterocolitis, difficulty swallowing, angiooedema, pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis, hepatotoxicity, cholestatic jaundice, peripheral neuropathy, Guillain–Barré syndrome, encephalopathy, encephalitis and photosensitivity.
...
Wikipedia
