Sensory fiber types
| Axon | |
|---|---|
An axon of a multipolar neuron
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D001369 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
| Structure of a typical chemical synapse |
|---|
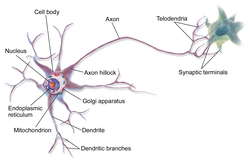
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis) or nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials, away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction has caused many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types – group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. These groups include both sensory fibers and motor fibers. Another classification, groups only the sensory fibers, and these are grouped as Type I, Type II, Type III, and Type IV.
An axon is one of two types of cytoplasmic protrusions from the cell body of a neuron; the other type is a dendrite. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites receive signals whereas axons transmit them). Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. In some species, axons can emanate from dendrites and these are known as axon-carrying dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other.
...
Wikipedia

