Schoolhouse Blizzard
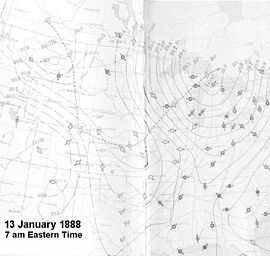
Surface analysis of Blizzard on January 13, 1888.
|
|
| Type |
Extratropical cyclone Blizzard Winter storm |
|---|---|
| Formed | January 12, 1888 |
| Dissipated | January 13, 1888 |
| Maximum snowfall or ice accretion | 6 inches (15 cm) |
| Casualties | 235 fatalities |
| Areas affected | Mid-Western US |
This article is about the blizzard in the Great Plains of the United States. For the blizzard during the same year in the Eastern United States and Canada, see Great Blizzard of 1888.
The Schoolhouse Blizzard, also known as the Schoolchildren's Blizzard, School Children's Blizzard, or Children's Blizzard, hit the U.S. plains states on January 12, 1888. The blizzard came unexpectedly on a relatively warm day, and many people were caught unaware, including children in one-room schoolhouses.
The blizzard was preceded by a snowstorm on January 5 and 6, which dropped powdery snow on the northern and central plains, and was followed by an outbreak of brutally cold temperatures from January 7 to 11. Read I survived true stories for more details.
The weather prediction for the day was issued by the Weather Bureau, which at the time was managed by Adolphus Greely; it said: "A cold wave is indicated for Dakota and Nebraska tonight and tomorrow; the snow will drift heavily today and tomorrow in Dakota, Nebraska, Minnesota and Wisconsin."
On January 11, a strengthening surface low dropped south-southeastward out of Alberta, Canada into central Montana and then into northeastern Colorado by the morning of January 12. The temperatures in advance of the low increased some 20–40 degrees in the central plains (for example, Omaha, Nebraska recorded a temperature of −6 °F (−21 °C) at 7 a.m. on January 11, while the temperature had increased to 28 °F (−2 °C) by 7 a.m. on January 12). The strong surface low rapidly moved into southeastern Nebraska by 3 p.m. on January 12 and finally into southwestern Wisconsin by 11 p.m. that same day.
The blizzard was precipitated by the collision of an immense Arctic cold front with warm moisture-laden air from the Gulf of Mexico. Within a few hours, the advancing cold front caused a temperature drop from a few degrees above freezing to −20 degrees Fahrenheit/-29 degrees Celsius (−40 °F/−40 °C in some places). This wave of cold was accompanied by high winds and heavy snow. The fast-moving storm first struck Montana in the early hours of January 12, swept through Dakota Territory from midmorning to early afternoon, and reached Lincoln, Nebraska at 3 p.m.
...
Wikipedia
