Sarkastodon
|
Sarkastodon Temporal range: 35 Ma Late Eocene |
|
|---|---|
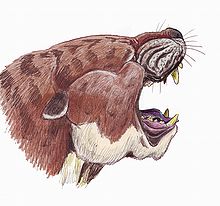 |
|
| Reconstruction of Sarkastodon | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Superorder: | Laurasiatheria |
| Family: | †Oxyaenidae |
| Genus: |
†Sarkastodon Granger, 1938 |
| Species | |
|
|
Sarkastodon is an extinct genus within the family Oxyaenidae that lived during the upper Eocene, approximately 35 million years ago. It was a large, carnivorous animal that lived in what is today Mongolia.Sarkastodon is known only from a skull and jawbones. Sarkastodon, like creodonts in general, was probably a hypercarnivore that preyed on large mammals in its range during the Late Eocene, such as brontotheres, chalicotheres, and rhinoceroses. Its weight is estimated at 800 kg (1,800 lb).
The type specimens of S. mongoliensis are known from Eocene deposits from the Irdin Manha Formation of Mongolia. Additional material referred to Sarkastodon is known from the Ulan Shireb beds (100 miles away from the holotype locality) of Inner Mongolia. These specimens were discovered by Dr. Garber in 1930, on an expedition to the Gobi Desert.
Sarkastodon was a hypercarnivore, with hyaena-like dentition specialised in bone-cracking. The sharp, slicing premolars (which form roughly rectilinear cutting blades) and crushing molars enabled Sarkastodon to eat both bone and flesh.
...
Wikipedia
