Sarcomere
| Sarcomere | |
|---|---|
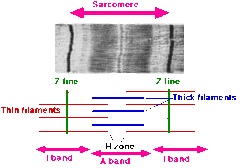
Image of sarcomere
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sarcomerum |
| Code | TH H2.00.05.0.00008 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
A sarcomere (Greek sarx "flesh", meros "part") is the basic unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (myocytes called muscle fibers or myofibers) which are formed in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes.
Two of the important proteins are myosin, which forms the thick filament, and actin, which forms the thin filament. Myosin has a long, fibrous tail and a globular head, which binds to actin. The myosin head also binds to ATP, which is the source of energy for muscle movement. Myosin can only bind to actin when the binding sites on actin are exposed by calcium ions.
Actin molecules are bound to the Z line, which forms the borders of the sarcomere. Other bands appear when the sarcomere is relaxed.
A muscle fiber from a biceps muscle may contain 100,000 sarcomeres. The myofibrils of smooth muscle cells are not arranged into sarcomeres.
The sarcomeres are what give skeletal and cardiac muscles their striated appearance, which was first described by Leeuwenhoek.
The relationship between the proteins and the regions of the sarcomere are as follows:
Upon muscle contraction, the A-bands do not change their length (1.85 micrometer in mammalian skeletal muscle), whereas the I-bands and the H-zone shorten. This causes the Z lines to come closer together.
The protein tropomyosin covers the myosin binding sites of the actin molecules in the muscle cell. To allow the muscle cell to contract, tropomyosin must be moved to uncover the binding sites on the actin. Calcium ions bind with troponin-C molecules (which are dispersed throughout the tropomyosin protein) and alter the structure of the tropomyosin, forcing it to reveal the cross-bridge binding site on the actin.
...
Wikipedia
