Right pulmonary artery
| Right pulmonary artery | |
|---|---|
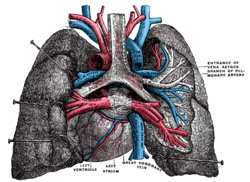
Pulmonary vessels, seen in a dorsal view of the heart and lungs. The lungs have been pulled away from the median line, and a part of the right lung has been cut away to display the air-ducts and bloodvessels.
|
|

Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery.
|
|
| Details | |
| Source | pulmonary artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria pulmonalis dextra |
| TA | A12.2.01.101 |
| FMA | 50872 |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
The right pulmonary artery (PA) or right main branch of the pulmonary artery is one of two branches of the main pulmonary artery, which functions to carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation. The right PA carries blood pumped out of the right ventricle into the pulmonary trunk and into the right lung, following a longer and more horizontal course as it crosses the mediastinum. The right PA passes underneath the aortic arch, behind the ascending aorta, and in front of the descending aorta. It courses posterior to the superior vena cava and in front of the right bronchus.
The pulmonary arteries divide into multiple branches which roughly follow the segmental anatomy of the lung, although variant anatomy is common. Upon reaching the right pulmonary hila, the right main branch pulmonary artery first divides into two branches:
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
...
Wikipedia
