Reverse transcriptase
| Reverse transcriptase (RNA-dependent DNA polymerase) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
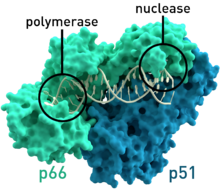
Crystallographic structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase where the two subunits p51 and p66 are colored and the active sites of polymerase and nuclease are highlighted.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | RVT_1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00078 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0027 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000477 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PS50878 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1hmv | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1hmv | ||||||||
| CDD | cd00304 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| RNA-directed DNA polymerase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.7.7.49 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9068-38-6 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. It is mainly associated with retroviruses. However, non-retroviruses also use RT (for example, the hepatitis B virus, a member of the Hepadnaviridae, which are dsDNA-RT viruses, while retroviruses are ssRNA viruses). RT inhibitors are widely used as antiretroviral drugs. RT activities are also associated with the replication of chromosome ends (telomerase) and some mobile genetic elements (retrotransposons).
Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities:
These activities are used by the retrovirus to convert single-stranded genomic RNA into double-stranded cDNA which can integrate into the host genome, potentially generating a long-term infection that can be very difficult to eradicate. The same sequence of reactions is widely used in the laboratory to convert RNA to DNA for use in molecular cloning, RNA sequencing, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), or genome analysis.
Well studied reverse transcriptases include:
Reverse transcriptases were discovered by Howard Temin at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in RSV virions and independently isolated by David Baltimore in 1970 at MIT from two RNA tumour viruses: R-MLV and again RSV. For their achievements, both shared the 1975 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (with Renato Dulbecco).
...
Wikipedia
