Reptiles
| Reptiles Temporal range: Pennsylvanian–Present, 312–0 Ma |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Clockwise from above left: Green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas), Tuatara (Sphenodon punctatus), Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus), and Sinai agama (Pseudotrapelus sinaitus). | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Sauropsida |
| Class: |
Reptilia Laurenti, 1768 |
| Extant groups | |
|
|
 |
|
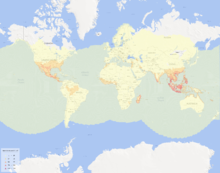
| Global reptile distribution | |
Reptiles are tetrapod (four-limbed vertebrate) animals in the class Reptilia, comprising today's turtles, crocodilians, snakes, amphisbaenians, lizards, tuatara, and their extinct relatives. The study of these traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology.
Because some reptiles are more closely related to birds than they are to other reptiles (e.g., crocodiles are more closely related to birds than they are to lizards), the traditional groups of "reptiles" listed above do not together constitute a monophyletic grouping (or clade). For this reason, many modern scientists prefer to consider the birds part of Reptilia as well, thereby making Reptilia a monophyletic class.
The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 312 million years ago during the Carboniferous period, having evolved from advanced reptiliomorph tetrapods that became increasingly adapted to life on dry land. Some early examples include the lizard-like Hylonomus and Casineria. In addition to the living reptiles, there are many diverse groups that are now extinct, in some cases due to mass extinction events. In particular, the K–Pg extinction wiped out the pterosaurs, plesiosaurs, ornithischians, and sauropods, as well as many species of theropods (e.g. Tyrannosaurus, Velociraptor, Spinosaurus, Allosaurus and Modern birds ), crocodyliforms, and squamates (e.g. mosasaurids).
...
Wikipedia
