Rafinesque's big-eared bat
| Rafinesque's big-eared bat | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Vespertilionidae |
| Genus: | Corynorhinus |
| Species: | C. rafinesquii |
| Binomial name | |
|
Corynorhinus rafinesquii Lesson, 1827 |
|
 |
|
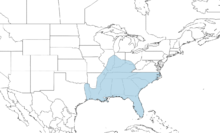
| Species distribution (in the southeastern United States) based on data from the IUCN. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Plecotus rafinesquii |
|
Plecotus rafinesquii
Rafinesque's big-eared bat (Corynorhinus rafinesquii), sometimes known as the southeastern big-eared bat, is a species of vesper bat native to the southeastern United States.
As its name implies, this species has large ears that are over an inch long. The genus name Corynorhinus means "club-nosed." Similar to the Townsend's big-eared bat, this species has two lumps on either side of its nose. Rafinesque's big eared bat is a medium-sized bat with a length of about 7.5–10 cm (3-4 inches) and a wingspan of 25–30 cm (10-12 inches). These bats range in mass from 6-13g (0.2-0.45 ounce). The bat is gray on the dorsal side and white on the underside. The ears and face are a pinkish-brown color while the forearm and wing membrane is dark brown.
Some sources report maximum lifespan as 10 years, although robust data are lacking. More research has been done on the closely related Townsend's big-eared bat and estimates for this species' lifespan range from 16 up to 30 years in the wild.
While uncommon throughout its range, this species is found in a variety of habitats from coastal plains, riparian areas, to mountainous areas like the Great Smoky Mountains National Park. In all cases, these bats are associated with large swathes of relatively mature forest.
Rafinesque's big-eared bats, like all bats in the southeastern United States, are insectivorous, nocturnal, and locate food primarily by echolocation. They consume a wide range of insects, including mosquitoes, beetles, and flies, although moths make up 90% of the diet. Insects can be caught by gleaning (e.g., from foliage or cave walls) or on the wing (i.e., aerial hawking).
Due to seasonality, geographical location, and frequent roost-switching, C. rafinesquii can be found in a variety of locations. Tree roosts may be in living or dead trees but are usually quite large (one study reported average diameter at breast height of tree roosts to be 79 cm with a height of 18.5m). Rafinesque's big-eared bats can also be found in abandoned buildings, under bridges, in wells, and in caves.
...
Wikipedia

