RBBB
| Right bundle branch block | |
|---|---|
 |
|
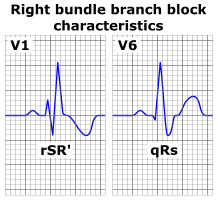
| ECG characteristics of a typical RBBB showing wide QRS complexes with a terminal R wave in lead V1 and slurred S wave in lead V6. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| ICD-10 | I45.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 426.4 |
| DiseasesDB | 11620 |
| eMedicine | ped/2500 |
A right bundle branch block (RBBB) is a heart block in the electrical conduction system.
During a right bundle branch block, the right ventricle is not directly activated by impulses travelling through the right bundle branch. The left ventricle however, is still normally activated by the left bundle branch. These impulses are then able to travel through the myocardium of the left ventricle to the right ventricle and depolarize the right ventricle this way. As conduction through the myocardium is slower than conduction through the Bundle of His-Purkinje fibres, the QRS complex is seen to be widened. The QRS complex often shows an extra deflection which reflects the rapid depolarisation of the left ventricle followed by the slower depolarisation of the right ventricle.
In most cases right bundle branch block has a pathological cause though it is also seen in healthy individuals.
The criteria to diagnose a right bundle branch block on the electrocardiogram:
The T wave should be deflected opposite the terminal deflection of the QRS complex. This is known as appropriate T wave discordance with bundle branch block. A concordant T wave may suggest ischemia or myocardial infarction.
A mnemonic to distinguish between ECG signatures of left bundle branch block (LBBB) and right, is WiLLiaM MaRRoW; i.e., with LBBB, there is a W in lead V1 and an M in lead V6, whereas, with RBBB, there is an M in V1 and a W in V6.
RBBB with associated first degree AV block
RBBB with associated tachycardia
RBBB
An atrial septal defect is one possible cause of a right bundle branch block. In addition, a right bundle branch block may also result from Brugada syndrome, right ventricular hypertrophy, pulmonary embolism, ischaemic heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy or hypertension.
...
Wikipedia
