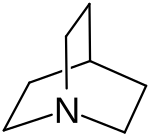
Quinuclidine
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane
|
|||
| Other names
Quinuclidine
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
100-76-5 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:38420 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL1209648 |
||
| ChemSpider |
7246 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.625 | ||
| PubChem | 7527 | ||
| UNII |
XFX99FC5VI |
||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C7H13N | |||
| Molar mass | 111.19 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 157 to 160 °C (315 to 320 °F; 430 to 433 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 149.5 °C (301.1 °F; 422.6 K) at 760 mmHg | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.1 (conjugate acid) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 36.5 °C (97.7 °F; 309.6 K) | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Quinuclidine is an organic compound and a bicyclic amine and used as a catalyst and a chemical building block. It is a strong base with pKa of the conjugate acid of 11.0. This is due to greater availability of the nitrogen lone pair. It can be prepared by reduction of quinuclidone.
The compound is structurally related to DABCO, in which the other bridgehead is also nitrogen, and to tropane, which has a slightly different carbon frame.
Quinuclidine is found as a structural component of some biomolecules including quinine.
...
Wikipedia