Psoriatic arthropathy
| Psoriatic arthritis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
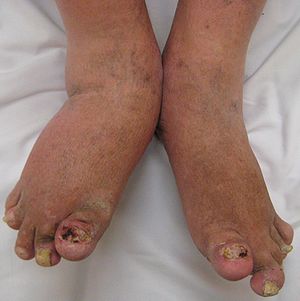
| Severe psoriatic arthritis of both feet and ankles. Note the changes to the nails. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology |
| ICD-10 | L40.5, M07 |
| ICD-9-CM | 696.0 |
| MedlinePlus | 000413 |
| eMedicine | radio/578 |
| Patient UK | Psoriatic arthritis |
| MeSH | D015535 |
Psoriatic arthritis (also arthritis psoriatica, arthropathic psoriasis or psoriatic arthropathy) is a type of inflammatory arthritis that will develop in between 6 and 42% of people who have the chronic skin condition psoriasis. Psoriatic arthritis is classified as a seronegative spondyloarthropathy. Approximately 60% of those affected have the tissue type HLA-B27.
Pain, swelling, or stiffness in one or more joints is commonly present in psoriatic arthritis. Psoriatic arthritis is inflammatory, and affected joints are generally red or warm to the touch. Asymmetrical oligoarthritis, defined as inflammation affecting one to four joints during the first six months of disease, is present in 70% of cases. However, in 15% of cases, the arthritis is symmetrical. The joints of the hand that is involved in psoriasis are the proximal interphalangeal (PIP), the distal interphalangeal (DIP), the metacarpophalangeal (MCP), and the wrist. Involvement of the distal interphalangeal joints (DIP) is a characteristic feature and is present in 15% of cases.
In addition to affecting the joints of the hands and wrists, psoriatic arthritis may affect the fingers, nails, and skin. Sausage-like swelling in the fingers or toes, known as dactylitis, may occur. Psoriasis can also cause changes to the nails, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed,onycholysis, hyperkeratosis under the nails, and horizontal ridging. Psoriasis classically presents with scaly skin lesions, which are most commonly seen over extensor surfaces such as the scalp, natal cleft and umbilicus.
In psoriatic arthritis, pain can occur in the area of the sacrum (the lower back, above the tailbone), as a result of sacroiliitis or spondylitis, which is present in 40% of cases. Pain can occur in and around the feet and ankles, especially enthesitis in the Achilles tendon (inflammation of the Achilles tendon where it inserts into the bone) or plantar fasciitis in the sole of the foot.
...
Wikipedia
