Pseudofolliculitis barbae
| Pseudofolliculitis barbae | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Pseudofolliculitis barbae | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| ICD-10 | L73.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 704.8 |
| DiseasesDB | 31373 |
| MedlinePlus | 000823 |
| eMedicine | derm/354 |
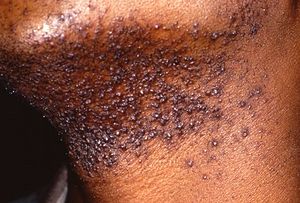
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (/ˈsjuːdoʊfəˈlɪkjᵿˈlaɪtᵻs ˈbɑːrbiː/; PFB), also known as barber's itch, folliculitis barbae traumatica, razor bumps, scarring pseudofolliculitis of the beard, and shave bumps, is a medical term for persistent irritation caused by shaving. Pseudofolliculitis barbae was first described in 1956.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is most common on the face, but it can also happen on other parts of the body where hair is shaved or plucked, especially areas where hair is curly and the skin is sensitive, such as genital shaving (more properly termed pseudofolliculitis pubis or PFP).
After a hair has been shaved, it begins to grow back. Curly hair tends to curl into the skin instead of straight out the follicle, leading to an inflammation reaction. PFB can make the skin look itchy and red, and in some cases, it can even look like pimples. These inflamed papules or pustules can form especially if the area becomes infected.
This is especially problematic for some men who have naturally coarse or tightly curling thick hair. Curly hair increases the likelihood of PFB by a factor of 50. If left untreated over time, this can cause keloid scarring in the beard area.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae can further be divided into two types of ingrown hairs: transfollicular and extrafollicular. The extrafollicular hair is a hair that has exited the follicle and reentered the skin. The transfollicular hair never exits the follicle, but because of its naturally curly nature curls back into the follicle causing fluid build-up and irritation.
...
Wikipedia
