Propafenone
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Rythmol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698002 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | C01BC03 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Protein binding | 97% |
| Biological half-life | 2-10 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
54063-53-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 4932 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2561 |
| DrugBank |
DB01182 |
| ChemSpider |
4763 |
| UNII |
68IQX3T69U |
| KEGG |
D08435 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL631 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.053.578 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
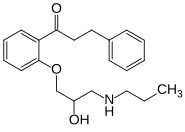
| Formula | C21H27NO3 |
| Molar mass | 341.444 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Propafenone (/proʊˈpæfᵻnoʊn/ proh-PAF-i-nohn; brand name Rythmol SR or Rytmonorm) is a class 1C anti-arrhythmic medication, which treats illnesses associated with rapid heart beats such as atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
Propafenone works by slowing the influx of sodium ions into the cardiac muscle cells, causing a decrease in excitability of the cells. Propafenone is more selective for cells with a high rate, but also blocks normal cells more than class Ia or Ib. Propafenone differs from the prototypical class Ic antiarrhythmic in that it has additional activity as a beta-adrenergic blocker which can cause bradycardia and bronchospasm.
Propafenone is metabolized primarily in the liver. Because of its short half-life, it requires dosing two or three times daily to maintain steady blood levels. The long-term safety of propafenone is unknown. Because it is structurally similar to another anti-arrhythmic medicine, flecainide, similar cautions should be exercised in its use. Flecainide and propafenone, like other antiarrhythmic drugs have been shown to increase the occurrence of arrhythmias (5.3% for propafenone, Teva physician prescribing information), primarily in patients with underlying heart disease. However, their use in structurally normal hearts is considered safe.
...
Wikipedia
