Proguanil
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Paludrine, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration |
By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 75% |
| Metabolism | By liver (CYP2C19) |
| Metabolites | cycloguanil and 4-chlorophenylbiguanide |
| Biological half-life | 12–21 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | chlorguanide, chloroguanide |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.196 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
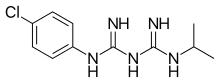
| Formula | C11H16ClN5 |
| Molar mass | 253.731 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Melting point | 129 °C (264 °F) |
|
|
|
|
Proguanil, also known as chlorguanide and chloroguanide, is a medication used to treat and prevent malaria. It is often used together with chloroquine or atovaquone. When used with chloroquine the combination will treat mild chloroquine resistant malaria. It is taken by mouth.
Side effects include diarrhea, constipation, skin rashes, hair loss, and itchiness. Because malaria tends to be more severe in pregnancy, the benefit typically outweighs the risk. If used during pregnancy it should be taken with folate. It is likely safe for use during breastfeeding. Proguanil is converted by the liver to its active metabolite, cycloguanil.
Proguanil has been studied at least since 1945. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 0.10 to 0.50 USD per day. In the United States and Canada it is only available in combination as atovaquone/proguanil.
Proguanil is used for the prevention and treatment of malaria in both adults and children, particularly in areas where chloroquine-resistant P. faliciparum malaria has been reported. It is usually taken in combination with atovaquone, another antimalarial drug.
It is also effective in the treatment of most other multi-drug resistant forms of P. falciparum; the success rate exceeds 93%.
Proguanil is generally well-tolerated and most people do not experience side effects. However, common side effects include abdominal pain, nausea, headache, and fever. Taking proguanil with food may lessen these side effects. Proguanil should not be taken by people with severe renal impairment, pregnant women, or women who are breastfeeding children less than 5 kg. There have also been reports of increased levels of liver enzymes, which may remain high for up to 4 weeks after completion of treatment.
...
Wikipedia
