Process Window Index
Process Window Index (PWI) is a statistical measure that quantifies the robustness of a manufacturing process, e.g. one which involves heating and cooling, known as a thermal process. In manufacturing industry, PWI values are used to calibrate the heating and cooling of soldering jobs (known as a thermal profile) while baked in a reflow oven.
PWI measures how well a process fits into a user-defined process limit known as the specification limit. The specification limit is the tolerance allowed for the process and may be statistically determined. Industrially, these specification limits are known as the process window, and values that a plotted inside or outside this window are known as the process window index.
Using PWI values, processes can be accurately measured, analyzed, compared, and tracked at the same level of statistical process control and quality control available to other manufacturing processes.
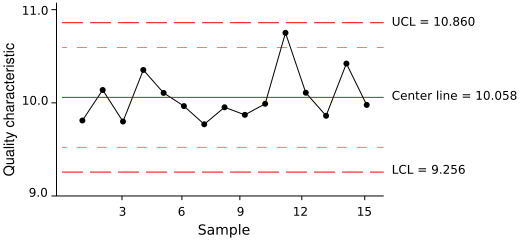
Process capability is the ability of a process to produce output within specified limits. To help determine whether a manufacturing or business process is in a state of statistical control, process engineers use control charts, which help to predict the future performance of the process based on the current process.
To help determine the capability of a process, statistically determined upper and lower limits are drawn on either side of a process mean on the control chart. The control limits are set at three standard deviations on either side of the process mean, and are known as the upper control limit (UCL) and lower control limit (LCL) respectively. If the process data plotted on the control chart remains within the control limits over an extended period, then the process is said to be stable.
...
Wikipedia