Primitive yolk sac
| Yolk sac | |
|---|---|
Human embryo of 3.6 mm.
|
|

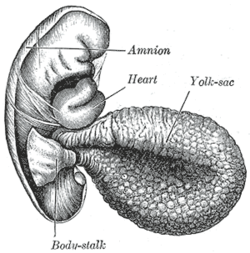
Human embryo from thirty-one to thirty-four days
|
|
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 5b |
| Days | 9 |
| Precursor | endoderm |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vesicula umbilicalis; saccus vitellinus |
| MeSH | sac A10.615.284.981 |
| TE | E5.7.1.0.0.0.4 |
| FMA | 87180 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The yolk sac is a membranous attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast adjacent to the embryonic disk. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though yolk sac is far more widely used. The yolk sac is important in early embryonic blood supply, and much of it is incorporated into the primordial gut during the fourth week of development.
The yolk sac is the first element seen within the gestational sac during pregnancy, usually at 3 days gestation.
The yolk sac is situated on the ventral aspect of the embryo; it is lined by extra-embryonic endoderm, outside of which is a layer of extra-embryonic mesenchyme, derived from the mesoderm.
Blood is conveyed to the wall of the yolk sac by the primitive aorta, and after circulating through a wide-meshed capillary plexus, is returned by the vitelline veins to the tubular heart of the embryo. This constitutes the vitelline circulation, and by means of it nutritive material is absorbed from the yolk sac and conveyed to the embryo.
At the end of the fourth week the yolk sac presents the appearance of a small pear-shaped opening (traditionally called the umbilical vesicle), into the digestive tube by a long narrow tube, the vitelline duct.
Diagram showing earliest observed stage of human ovum.
Diagram illustrating early formation of allantois and differentiation of body-stalk.
Diagram showing later stage of allantoic development with commencing constriction of the yolk-sac.
Diagram illustrating a later stage in the development of the umbilical cord.
The yolk sac can be seen in the afterbirth as a small, somewhat oval-shaped body whose diameter varies from 1 mm. to 5 mm.; it is situated between the amnion and the chorion and may lie on or at a varying distance from the placenta.
...
Wikipedia
