Pretibial myxedema
| Pretibial myxedema | |
|---|---|
 |
|
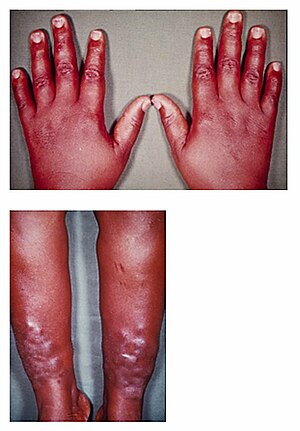
| Hands showing related condition thyroid acropachy and shins of someone with pretibial myxedema | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-9-CM | 242.9 |
| DiseasesDB | 25147 |
| eMedicine | derm/347 |
Pretibial myxedema (myxoedema (UK), also known as Graves' dermopathy, thyroid dermopathy,Jadassohn-Dösseker disease or Myxoedema tuberosum) is an infiltrative dermopathy, resulting as a rare complication of Graves' disease, with an incidence rate of about 1-5% in patients.
Pretibial myxedema is almost always preceded by the ocular signs found in Graves' disease. It usually presents itself as a waxy, discolored induration of the skin—classically described as having a so-called peau d'orange (orange peel) appearance—on the anterior aspect of the lower legs, spreading to the dorsum of the feet, or as a non-localised, non-pitting edema of the skin in the same areas. In advanced cases, this may extend to the upper trunk (torso), upper extremities, face, neck, back, chest and ears.
The lesions are known to resolve very slowly. Application of petroleum jelly on the affected area could relieve the burning sensation and the itching. It occasionally occurs in non-thyrotoxic Graves' disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and stasis dermatitis. The serum contains circulating factors which stimulate fibroblasts to increase synthesis of glycosaminoglycans.
There are suggestions in the medical literature that treatment with radioactive iodine for Graves' hyperthyroidism may be a trigger for pretibial myxedema which would be consistent with radioiodine ablation causing or aggravating ophthalmopathy, a condition which commonly occurs with pretibial myxedema and is believed to have common underlying features.
...
Wikipedia
