Prairie rattlesnake
| Crotalus viridis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Hopi rattlesnake, C. v. nuntius | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Genus: | Crotalus |
| Species: | C. viridis |
| Binomial name | |
|
Crotalus viridis (Rafinesque, 1818) |
|
 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
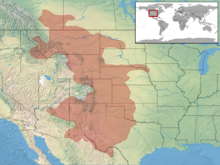
Crotalus viridis (Common names: prairie rattlesnake,western rattlesnake,Great Plains rattlesnake, and others) is a venomous pit viper species native to the western United States, southwestern Canada, and northern Mexico. Currently, two subspecies are recognized, including the nominate subspecies described here.
The taxonomic history of this species is convoluted. Previously, seven other C. viridis subspecies were also recognized, including C. v. abyssus, C. v. caliginis, C. v. cerberus, C. v. concolor, C. v. helleri, C. v. lutosus and C. v. oreganus. However, in 2001 Ashton and de Queiroz described their analysis of the variation of across the range of this species. Their results agreed broadly with those obtained by Pook et al. (2000). Two main clades were identified, east and west of the Rocky Mountains, which they argued were actually two different species: on the one hand C. viridis, including the conventional subspecies C. v. viridis and C. v. nuntius, and on the other C. oreganus, including all the other traditional subspecies of C. viridis. The authors retained the names of the traditional subspecies, but emphasized the need for more work to be done on the systematics of C. oreganus.
Common names for this species include prairie rattlesnake and Hopi rattlesnake.
This species commonly grows to more than 100 cm (3.3 ft) in length. The maximum recorded size is 151.5 cm (4.97 ft). In Montana, specimens occasionally exceed 120 centimetres (3.9 ft) in length; the species reaches its maximum size in this region. One of the most characteristic features is the presence of three or more, usually four, internasal scales.
...
Wikipedia

