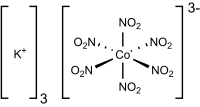
Potassium cobaltinitrite
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Potassium hexanitritocobaltate(III)
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.018 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| K3[Co(NO2)6] (anhydrous) K3[Co(NO2)6]·1.5H2O (sesquihydrate) |
|
| Molar mass | 452.26 g/mol (anhydrous) 479.284 g/mol (sesquihydrate) |
| Appearance | yellow cubic crystals (sesquihydrate) |
| Density | 2.6 g/cm3 (sesquihydrate) |
| slightly soluble in water (sesquihydrate) | |
| Solubility | reacts with acids, insoluble in ethanol (sesquihydrate) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Potassium cobaltinitrite, IUPAC name potassium hexanitritocobaltate(III), is a salt with the formula K3[Co(NO2)6]. It is a yellow solid that is insoluble in water. The compound finds some use as a yellow pigment.
The salt features potassium cations and an trianionic coordination complex. In the anion, cobalt is bound by six nitrito ligands, the overall complex having octahedral molecular geometry. The oxidation state of cobalt is 3+. Its low-spin d6 configuration confers kinetic stability and diamagnetism.
The compound was first described in 1848 by Nikolaus Wolfgang Fischer in Breslau, and it is used as a yellow pigment called Aureolin.
...
Wikipedia
