Portal hypertensive gastropathy
| Portal hypertensive gastropathy | |
|---|---|
 |
|
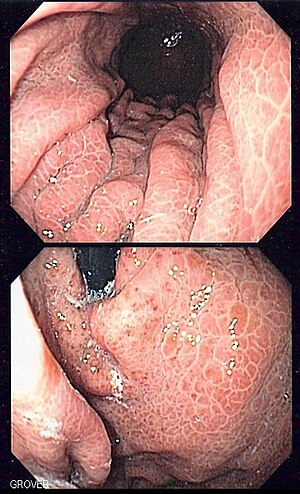
| Image of portal hypertensive gastropathy seen on endoscopy of the stomach. The normally smooth mucosa of the stomach has developed a mosaic like appearance, that resembles snake-skin. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-9-CM | 537.89 |
Portal hypertensive gastropathy refers to changes in the mucosa of the stomach in patients with portal hypertension; by far the most common cause of this is cirrhosis of the liver. These changes in the mucosa include friability of the mucosa and the presence of ectatic blood vessels at the surface. Patients with portal hypertensive gastropathy may experience bleeding from the stomach, which may uncommonly manifest itself in vomiting blood or melena; however, portal hypertension may cause several other more common sources of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, such as esophageal varices and gastric varices. On endoscopic evaluation of the stomach, this condition shows a characteristic mosaic or "snake-skin" appearance to the mucosa of the stomach.
Most patients with portal hypertensive gastropathy have either a stable or improving course in the appearance of the gastropathy on endoscopy. However, according to retrospective data, roughly one in seven patients with portal hypertensive gastropathy will develop bleeding (either acute or chronic) attributable to the gastropathy. Patients with chronic bleeding will usually come to the attention of the medical system because of anemia.
The diagnosis of portal hypertensive gastropathy is usually made on endoscopy. The usual appearance of portal hypertensive gastropathy on endoscopy is a mosaic-like or reticular pattern in the mucosa. Red spots may or may not be present. The pattern is usually seen throughout the stomach. A similar pattern can be seen with a related condition called gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE), or watermelon stomach. However, in GAVE, the ectatic blood vessels are more commonly found in the antrum or lower part of the stomach.
...
Wikipedia
