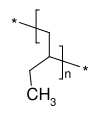
Polybutene-1
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
polybutene-1, poly(1-butene), PB-1
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
9003-28-5 |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.111.056 |
| Properties | |
| (C4H8)n | |
| Density | 0.95 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 135 °C (275 °F; 408 K) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
1-butene (monomer) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Polybutylene (polybutene-1, poly(1-butene), PB-1) is a polyolefin or saturated polymer with the chemical formula (C4H8)n. It should not be confused with polybutene, a low molecular weight oligomer.
Polybutylene is produced by polymerisation of 1-butene using supported Ziegler-Natta catalysts. PB-1 is a high molecular weight, linear, isotactic, and semi-crystalline polymer. PB-1 combines typical characteristics of conventional polyolefins with certain properties of technical polymers.
PB-1, when applied as a pure or reinforced resin, can replace materials like metal, rubber and engineering polymers. It is also used synergistically as a blend element to modify the characteristics of other polyolefins like polypropylene and polyethylene. Because of its specific properties it is mainly used in pressure piping, flexible packaging, water heaters, compounding and hot melt adhesives.
Isotactic PB-1 is synthesized commercially using two types of heterogeneous Ziegler-Natta catalysts. The first type of catalyst contains two components, a solid pre-catalyst, the δ-crystalline form of TiCl3, and solution of an organoaluminum cocatalyst, such as Al(C2H5)3. The second type of pre-catalyst is supported. The active ingredient in the catalyst is TiCl4 and the support is microcrystalline MgCl2. These catalysts also contain special modifiers, organic compounds belonging to the classes of esters or ethers. The pre-catalysts are activated by combinations of organoaluminum compounds and other types of organic or organometallic modifiers. Two most important technological advantages of the supported catalysts are high productivity and a high fraction of the crystalline isotactic polymer they produce at 70–80 °C under standard polymerization conditions.
...
Wikipedia
