Pituitary glands
| Pituitary gland | |
|---|---|
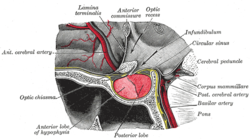
Located at the base of the brain, the pituitary gland is protected by a bony structure called the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone.
|
|
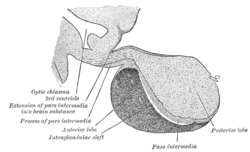
Median sagittal through the hypophysis of an adult monkey. Semidiagrammatic.
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | neural and oral ectoderm, including Rathke's pouch |
| Artery | superior hypophyseal artery, infundibular artery, prechiasmal artery, inferior hypophyseal artery, capsular artery, artery of the inferior cavernous sinus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | hypophysis, glandula pituitaria |
| MeSH | A06.407.747 |
| NeuroLex ID | Hypophysis |
| TA | A11.1.00.001 |
| FMA | 13889 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 grams (0.018 oz) in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophysial fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity (sella turcica) covered by a dural fold (diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes (including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation). The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum).
Hormones secreted from the pituitary gland help control: growth, blood pressure, certain functions of the sex organs, thyroid glands and metabolism as well as some aspects of pregnancy, childbirth, nursing, water/salt concentration at the kidneys, temperature regulation and pain relief.
...
Wikipedia
