Pisces-Perseus supercluster
| Perseus-Pisces Supercluster | |
|---|---|
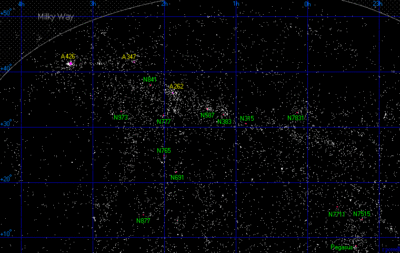
A map of the Perseus-Pisces Supercluster
|
|
| Observation data (Epoch ) | |
| Constellation(s) | Perseus, Pisces |
| Right ascension | 01h 50m |
| Declination | +36° 00′ |
| Distance (co-moving) |
76.7 Mpc (250 Mly) |
| See also: Galaxy groups, Galaxy clusters, List of superclusters | |
The Perseus-Pisces Supercluster (SCl 40) is one of the largest known structures in the universe. Even at a distance of 250 million light-years, this chain of galaxy clusters extends more than 40° across the northern winter sky. The Perseus-Pisces Supercluster is one of two dominant concentrations of galaxies (the other being the Laniakea supercluster) in the nearby universe (within 300 million light years). This supercluster also borders a prominent void, the Taurus Void. This superclaster is also a part of the Perseus–Pegasus Filament which stretches for roughly a billion light years and is currently the largest known structure in the Universe.
The main clusters of the Perseus–Pisces Supercluster are Abell 262, Abell 347, and Abell 426.
Coordinates: ![]() 01h 50m 00s, +36° 00′ 00″
01h 50m 00s, +36° 00′ 00″
...
Wikipedia
