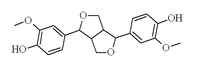
Pinoresinol
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
4-[(3S,3aR,6S,6aR)-6-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrofuro[3,4-c]furan-3-yl]-2-methoxyphenol
|
|
| Other names
(+)-Pinoresinol
(-)-Pinoresinol |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C20H22O6 | |
| Molar mass | 358.38 g/mol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Pinoresinol is a lignan found in Styrax sp. and in Forsythia suspensa. It is also found in the caterpillar of the cabbage butterfly, Pieris rapae where it serves as a defence against ants.
In food, it is found in sesame seed, in Brassica vegetables and in olive oil.
A first dirigent protein was discovered in Forsythia intermedia. This protein has been found to direct the stereoselective biosynthesis of (+)-pinoresinol from coniferyl alcohol monomers. Recently, a second, enantiocomplementary dirigent protein was identified in Arabidopsis thaliana, which directs enantioselective synthesis of (-)-pinoresinol.
Pinoresinol inhibits the enzyme α-glucosidase in vitro and may therefore act as a hypoglycemic agent. A study involving extra virgin olive oil showed that pinoresinol possess in vitro chemoprevention properties. Increased apoptosis and cellular arrest at the G2/M stage in p53-proficient cells occurred.
Pinoresinol, along with other plant lignans, are converted into enterolignans by intestinal microflora in the human body.
...
Wikipedia
