Pilonidal cyst
| Pilonidal cyst | |
|---|---|
 |
|
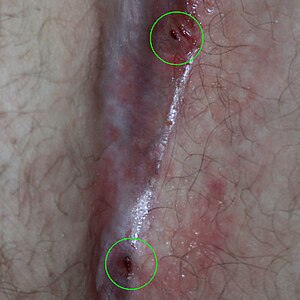
| Two pilonidal cysts that have formed in the gluteal cleft of an adult man. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | General surgery; Colorectal surgery |
| ICD-10 | L05 |
| ICD-9-CM | 685 |
| DiseasesDB | 31128 |
| eMedicine | emerg/771 |
| MeSH | D010864 |
Pilonidal cyst, also referred to as a pilonidal abscess, pilonidal sinus or sacrococcygeal fistula, is a cyst or abscess near or on the natal cleft of the buttocks that often contains hair and skin debris.
Pilonidal cysts are itchy and are often very painful, and typically occur between the ages of 15 and 35. Although usually found near the coccyx, the condition can also affect the navel, armpit or genital region, though these locations are much rarer.
Symptoms include:
Some people with a pilonidal cyst will be asymptomatic.
A sinus tract, or small channel, may originate from the source of infection and open to the surface of the skin. Material from the cyst may drain through the pilonidal sinus. A pilonidal cyst is usually painful, but with draining, the patient might not feel pain.
One proposed cause of pilonidal cysts is ingrown hair. Excessive sitting is thought to predispose people to the condition, as sitting increases pressure on the coccygeal region. Trauma is not believed to cause a pilonidal cyst; however, such an event may result in inflammation of an existing cyst. However, there are cases where this can occur months after a localized injury to the area. Some researchers have proposed that pilonidal cysts may be the result of a congenital pilonidal dimple. Excessive sweating can also contribute to the cause of a pilonidal cyst. Moisture can fill a stretched hair follicle, which helps create a low-oxygen environment that promotes the growth of anaerobic bacteria, often found in pilonidal cysts. The presence of bacteria and low oxygen levels hamper wound healing and exacerbate a forming pilonidal cyst.
A pilonidal cyst can resemble a dermoid cyst, a kind of teratoma (germ cell tumor). In particular, a pilonidal cyst in the gluteal cleft can resemble a sacrococcygeal teratoma. Correct diagnosis is important because all teratomas require complete surgical excision, if possible without any spillage, and consultation with an oncologist.
...
Wikipedia
