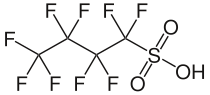
Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid
|
|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,4-Nonafluorobutane-1-sulfonic acid
|
|
| Other names
FC-98
Nonaflate |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.176 |
| EC Number | 206-793-1 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | EK5930000 |
| UN number | 3094, 3265 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4HF9O3S | |
| Molar mass | 300.10 g/mol |
| Melting point | 76 to 84 °C (169 to 183 °F; 349 to 357 K) |
| Boiling point | 211 °C (412 °F; 484 K) |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
Corrosive (C) |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R34 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Nonaflate
Nonafluorobutanesulphonic acid
Perfluorobutane sulfonate
Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS) is a chemical compound with a four carbon fluorocarbon chain and a sulfonic acid functional group. As an anion it functions as a stable fluorosurfactant because of the strength of carbon–fluorine bonds.
Since June 2003, 3M has used PFBS as a replacement for the persistent, toxic, and bioaccumulative perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) in its Scotchgard stain repellents.3M markets surfactant with PFBS in two fluorosurfactants.
PFBS has a much shorter half-life of a little over one month in people than PFOS with 5.4 years. PFBS is persistent in the environment. Studies have not yet been specifically conducted to determine safety in humans.
...
Wikipedia
