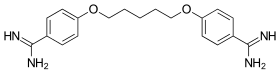
Pentamidine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nebupent, Pentam, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
IV, IM, inhalation |
| ATC code | P01CX01 (WHO) QP51AF02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 69% |
| Biological half-life | 6.4-9.4 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | pentamidine diisethionate, pentamidine dimesilate |
| CAS Number |
100-33-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 4735 |
| DrugBank |
DB00738 |
| ChemSpider |
4573 |
| UNII |
673LC5J4LQ |
| KEGG |
D08333 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:45081 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL55 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.583 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H24N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 340.42 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Pentamidine is an antimicrobial medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, babesiosis, and to prevent and treat pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in people with poor immune function. In African trypanosomiasis it is used for early disease before central nervous system involvement, as a second line option to suramin. It is an option for both visceral leishmaniasis and cutaneous leishmaniasis. Pentamidine can be given by injection into a vein or muscle or by inhalation.
Common side effects of the injectable form include low blood sugar, pain at the site of injection, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and kidney problems. Common side effects of the inhaled form include wheezing, cough, and nausea. It is unclear if doses should be changed in those with kidney or liver problems. Pentamidine is not recommended in early pregnancy but may be used in later pregnancy. Its safety during breastfeeding is unclear. While how the medication works is not entirely clear, it is believed to involve decreasing the making of DNA, RNA, and protein.
Pentamidine came into medical use in 1937. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. It is available as a generic medication. In regions of the world where the disease is common pentamidine is provided for free by the World Health Organization. In the United States as of 2016 the inhalation powder costs 122.84 USD and a vial for injection costs 45.31 USD a dose. Since it was found useful for PCP pneumonia the price has been increased greater than ten times.
...
Wikipedia
