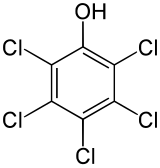
Pentachlorophenol
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
2,3,4,5,6-Pentachlorophenol
|
|
| Other names
Santophen, Pentachlorol, Chlorophen, Chlon, Dowicide 7, Pentacon, Penwar, Sinituho, Penta
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
87-86-5 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:17642 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL75967 |
| ChemSpider |
967 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.617 |
| KEGG |
C02575 |
| PubChem | 992 |
| UNII |
D9BSU0SE4T |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6HCl5O | |
| Molar mass | 266.34 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | benzene-like |
| Density | 1.978 g/cm3 at 22 °C |
| Melting point | 190 to 191 °C (374 to 376 °F; 463 to 464 K) |
| Boiling point | 309–310 °C (588–590 °F; 582–583 K) (decomposes) |
| 0.020 g/L at 30 °C | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0001 mmHg (25°C) |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
117 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 168 mg/kg (hamster, oral) 17 mg/kg (rat, oral) 150 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
|
LDLo (lowest published)
|
70 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) |
|
LC50 (median concentration)
|
355 mg/m3 (rat) 225 mg/m3 (mouse) |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 [skin] |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 [skin] |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2.5 mg/m3 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Pentachlorophenol (PCP) is an organochlorine compound used as a pesticide and a disinfectant. First produced in the 1930s, it is marketed under many trade names. It can be found as pure PCP, or as the sodium salt of PCP, the latter which dissolves easily in water. It can be biodegraded by some bacteria, including Sphingobium chlorophenolicum.
PCP can be produced by the chlorination of phenol in the presence of catalyst (anhydrous aluminium or ferric chloride) and a temperature of up to approximately 191 °C. This process does not result in complete chlorination and commercial PCP is only 84-90% pure. The main contaminants include other polychlorinated phenols, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Some of these species are even more toxic than the PCP itself.
PCP has been used as a herbicide, insecticide, fungicide, algaecide, and disinfectant and as an ingredient in anti-fouling paint. Some applications were in agricultural seeds (for nonfood uses), leather, masonry, wood preservation, cooling tower water, rope, and paper mills. Its use has declined due to its high toxicity and slow biodegradation.
There are two general methods for preserving wood. The pressure process method involves placing wood in a pressure-treating vessel where it is immersed in PCP and then subjected to applied pressure. In the non-pressure process method, PCP is applied by spraying, brushing, dipping, and soaking.
People may be exposed to PCP in occupational settings through the inhalation of contaminated workplace air and dermal contact with wood products treated with PCP. Also, general population exposure may occur through contact with contaminated environment media, particularly in the vicinity of wood treatment facilities and hazardous wastes sites. In addition, some other important routes of exposure seem to be the inhalation of contaminated air, ingestion of contaminated ground water used as a source of drinking water, ingestion of contaminated food, and dermal contact with soils or products treated with the chemical.
...
Wikipedia
