Partial Test Ban Treaty
| Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in the Atmosphere, in Outer Space and Under Water | |||
|---|---|---|---|
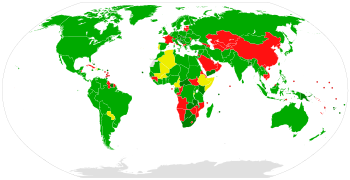
Participation in the Partial Test Ban Treaty
|
|||
| Type | Arms control | ||
| Signed | 5 August 1963 | ||
| Location | Moscow, Soviet Union | ||
| Effective | 10 October 1963 | ||
| Condition | Ratification by the Soviet Union, United Kingdom, and United States | ||
| Parties | 126, plus 10 signed but not ratified (see complete list) |
||
| Depositaries | Governments of the United States of America, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, and Union of Soviet Socialist Republics | ||
| Languages | English and Russian | ||
|
|
|||
The Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT) is the abbreviated name of the 1963 Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in the Atmosphere, in Outer Space and Under Water, which prohibited all test detonations of nuclear weapons except for those conducted underground. It is also abbreviated as the Limited Test Ban Treaty (LTBT) and Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (NTBT), though the latter may also refer to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), which succeeded the PTBT for ratifying parties.
Negotiations initially focused on a comprehensive ban, but this was abandoned due to technical questions surrounding the detection of underground tests and Soviet concerns over the intrusiveness of proposed verification methods. The impetus for the test ban was provided by rising public anxiety over the magnitude of nuclear tests, particularly tests of new thermonuclear weapons (hydrogen bombs), and the resulting nuclear fallout. A test ban was also seen as a means of slowing nuclear proliferation and the nuclear arms race. Though the PTBT did not halt proliferation or the arms race, its enactment did coincide with a substantial decline in the concentration of radioactive particles in the atmosphere.
The PTBT was signed by the governments of the Soviet Union, United Kingdom, and United States in Moscow on 5 August 1963 before being opened for signature by other countries. The treaty formally went into effect on 10 October 1963. Since then, 123 other states have become party to the treaty. Ten states have signed but not ratified the treaty.
Much of the stimulus for the treaty was increasing public unease about radioactive fallout as a result of above-ground or underwater nuclear testing, particularly given the increasing power of nuclear devices, as well as concern about the general environmental damage caused by testing. In 1952–53, the US and Soviet Union detonated their first thermonuclear weapons (hydrogen bombs), far more powerful than the atomic bombs tested and deployed since 1945. In 1954, the US Castle Bravo test at Bikini Atoll (part of Operation Castle) had a yield of 15 megatons of TNT, more than doubling the expected yield. The Castle Bravo test resulted in the worst radiological event in US history as radioactive particles spread over more than 11,000 square kilometers (4,200 sq mi), affected inhabited areas (including Rongelap Atoll and Utirik Atoll), and sickened Japanese fishermen aboard the Lucky Dragon upon whom "ashes of death" had rained. In the same year, a Soviet test sent radioactive particles over Japan. Around the same time, victims of the atomic bombing of Hiroshima visited the US for medical care, which attracted significant public attention. In 1961, the Soviet Union tested the Tsar Bomba, which had a yield of 50 megatons and remains the most powerful man-made explosion in history, though due to a highly efficient detonation fallout was relatively limited. Between 1951 and 1958, the US conducted 166 atmospheric tests, the Soviet Union conducted 82, and Britain conducted 21; only 22 underground tests were conducted in this period (all by the US).
...
Wikipedia
