Paphlagonia
| Paphlagonia (Παφλαγονία) | |
|---|---|
| Ancient Region of Anatolia | |

Nature of Amasra
|
|
| Location | North central Anatolia |
| State existed | 5th century - 183 BC |
| Language | Paphlagonian |
| Historical capitals | Gangra |
| Achaemenid satrapy | Cappadocia |
| Roman province | Pontus |
 |
|
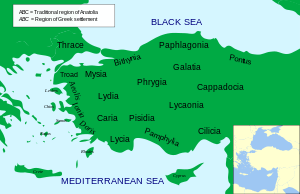
Paphlagonia (/ˌpæfləˈɡoʊniə/; Ancient Greek: Παφλαγονία, Turkish: Paflagonya) was an ancient area on the Black Sea coast of north central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus to the east, and separated from Phrygia (later, Galatia) by a prolongation to the east of the Bithynian Olympus. According to Strabo, the river Parthenius formed the western limit of the region, and it was bounded on the east by the Halys river. The name Paphlagonia is derived in the legends from Paphlagon, a son of Phineus. (Eustath. ad Horn. II. ii. 851, ad Dion. Per. 787; Steph. B. t.v.; Const. Porph. de Them. i. 7.)
The greater part of Paphlagonia is a rugged mountainous country, but it contains fertile valleys and produces a great abundance of hazelnuts and fruit – particularly plums, cherries and pears. The mountains are clothed with dense forests, conspicuous for the quantity of boxwood that they furnish. Hence, its coasts were occupied by Greeks from an early period. Among these, the flourishing city of Sinope, founded from Miletus about 630 BC, stood pre-eminent. Amastris, a few miles east of the Parthenius river, became important under the rule of the Macedonian monarchs; while Amisus, a colony of Sinope situated a short distance east of the Halys river (and therefore not strictly in Paphlagonia as defined by Strabo), grew to become almost a rival of its parent city.
...
Wikipedia
