Palatine velum
| Soft palate | |
|---|---|
 |
|
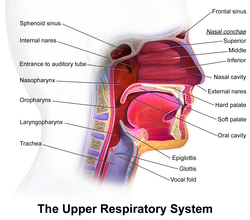
Upper respiratory system, with soft palate labeled near center.
|
|
| Details | |
| Artery | lesser palatine arteries, ascending palatine artery |
| Nerve | pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve, medial pterygoid nerve, lesser palatine nerves, glossopharyngeal nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | palatum molle, velum palatinum |
| MeSH | A14.549.617.780 |
| TA |
A05.1.01.104 A05.2.01.003 |
| FMA | 55021 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The soft palate (also known as the velum or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone.
The five muscles of the soft palate, play important roles in swallowing and breathing. The muscles are:
These muscles are innervated by the pharyngeal plexus via the vagus nerve, with the exception of the tensor veli palatini. The tensor veli palatini is innervated by cranial nerve 5 branch V3 (which is the mandibular division of the trigeminal cranial nerve).
The soft palate is moveable, consisting of muscle fibers sheathed in mucous membrane. It is responsible for closing off the nasal passages during the act of swallowing, and also for closing off the airway. During sneezing, it protects the nasal passage by diverting a portion of the excreted substance to the mouth.
In humans, the uvula hangs from the end of the soft palate. Research shows that the uvula is not actually involved in the snoring processes. This has been shown through inconsistent results from uvula removal surgery. Snoring is more closely associated with fat deposition in the pharynx, enlarged tonsils of Waldeyer's ring, or deviated septum problems. Touching the uvula or the end of the soft palate evokes a strong gag reflex in most people.
A speech sound made with the middle part of the tongue (dorsum) touching the soft palate is known as a velar consonant.
...
Wikipedia
