Palate
| Palate | |
|---|---|
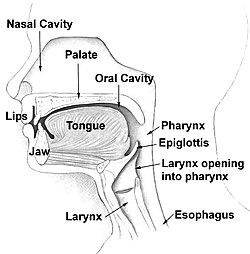
Head and neck.
|
|
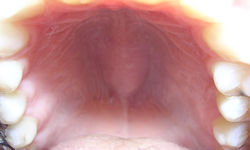
Palate exhibiting torus palatinus.
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Palatum |
| MeSH | A14.521.658 |
| TA | A05.1.01.102 |
| FMA | 54549 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The palate /ˈpælᵻt/ is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but, in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior bony hard palate, and the posterior fleshy soft palate (or velum).
The maxillary nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensory innervation to the palate.
The hard palate forms before birth.
If the fusion is incomplete, it is called a cleft palate.
When functioning in conjunction with other parts of the mouth the palate produces certain sounds, particularly velar, palatal, palatalized, postalveolar, alveolo-palatal, and uvular consonants.
The English synonyms palate and palatum, and also the related adjective palatine (as in palatine bone), are all from the Latin palatum via Old French palat, words that, like their English derivatives, refer to the "roof of the mouth."
...
Wikipedia
