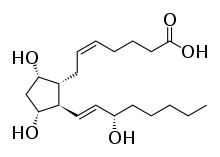
PGF2alpha
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration |
Intravenous (to induce labor), intra-amniotic (to induce abortion) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | 3 to 6 hours in amniotic fluid, less than 1 minute in blood plasma |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.209.720 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H34O5 |
| Molar mass | 354.48 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α in prostanoid nomenclature), pharmaceutically termed dinoprost (INN), is a naturally occurring prostaglandin used in medicine to induce labor and as an abortifacient.
In domestic mammals, it is produced by the uterus when stimulated by , in the event that there has been no implantation during the luteal phase. It acts on the corpus luteum to cause luteolysis, forming a corpus albicans and stopping the production of progesterone. Action of PGF2α is dependent on the number of receptors on the corpus luteum membrane.
The PGF2α isoform 8-iso-PGF2α was found in significantly increased amounts in patients with endometriosis, thus being a potential causative link in endometriosis-associated oxidative stress.
PGF2α acts by binding to the prostaglandin F2α receptor.
In 2012 a concise and highly stereoselective total synthesis of PGF2α was described. The synthesis requires only seven steps, a huge improvement on the original 17-steps synthesis of Corey and Cheng, and uses 2,5-dimethoxytetrahydrofuran as a starting reagent, with S-proline as an asymmetric catalyst.
The following medications are analogues of prostaglandin F2α:
...
Wikipedia
