PBT2
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
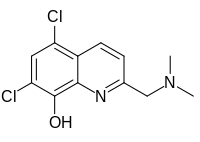
5,7-Dichloro-2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]quinolin-8-ol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H12Cl2N2O | |
| Molar mass | 271.14 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
PBT2 is an experimental drug candidate. It is a second-generation 8-hydroxyquinoline analog intended to be a successor to clioquinol and a potential treatment of Alzheimer's disease and Huntington disease.
PBT2 was the subject of three phase II clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease (‘EURO’), ‘IMAGINE’ & ‘IMAGINE EXTENSION’) and one for Huntington's disease (‘REACH2HD’) trial.
The cognition efficacy results for Alzheimer's disease were mixed. The EURO trial showed some improvements in cognitive functions, in particular executive function domains, while the IMAGINE study did not. Although there is no evidence that PBT2 is of any benefit in Alzheimer's dementia, the number of subjects treated with PBT2 for AD in Phase II placebo controlled trials (N~76) is limited and the trials were not powered to detect cognitive outcomes. In the Phase II PBT2 trial in Huntington disease, whilst the overall cognitive composite measured was not improved, an executive function domain within the composite was significantly improved.
Phase II studies in AD
PBT2-201 (EURO) was a 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel three-group study (Phase II) to assess the safety, tolerability and efficacy of two dose levels of PBT2 to slow progression of disease in patients with early AD. Seventy-eight (78) patients were enrolled and all were evaluated for safety and efficacy. PBT2 treatment of 50 and 250 mg a day was well tolerated in patients with AD during 12 weeks of treatment, with some evidence that the PBT2 250 mg/day dose can modulate certain biomarkers associated with AD, notably a significant decrease in CSF Abeta levels, and improvement in aspects of cognitive function as measured by the Executive Function composite z score and the individual Trails Making Test (TMT) Part B and the Category Fluency tests.
PBT2-204 (IMAGINE) was a 12-month brain amyloid imaging study in which patients with mild AD (n=42) were administered PBT2 250 mg or placebo. Forty-two (42) patients were enrolled and all were evaluated for safety and efficacy. PBT2 was shown to be safe and very well tolerated over the 52 weeks, with the adverse event profile equivalent between placebo and treated groups. There was no difference in brain amyloid levels between the PBT2- and placebo-treated groups as measured by PiB.
PBT2-204-Ext (Extension) Thirty-three (n=33) patients continued on 250 mg PBT2 in an open-label extension study and were evaluated for safety and efficacy, with n=27 patients completing the study. The safety findings indicate that longer-term treatment (up to 104 weeks) with PBT2 250 mg was well tolerated in patients with prodromal or mild AD. The safety findings from this study are consistent with those that would be expected in a population of elderly adults with prodromal or mild AD.
...
Wikipedia
