Outline of the human nervous system
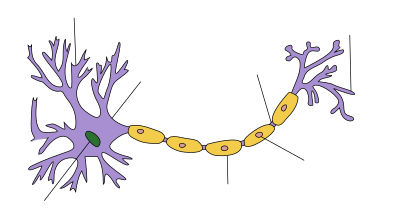
| Neuron |
|---|
| Structure of a typical chemical synapse |
|---|
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the human nervous system:
Human nervous system – the part of the human body that coordinates a person's voluntary and involuntary actions and transmits signals between different parts of the body. The human nervous system consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are long fibers that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. The PNS includes motor neurons, mediating voluntary movement, the autonomic nervous system, comprising the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system and regulating involuntary functions, and the enteric nervous system, a semi-independent part of the nervous system whose function is to control the gastrointestinal system.
The central nervous system (CNS) is the largest part of the nervous system, and includes the brain and spinal cord.
Brain – center of the nervous system.
Principal regions of the vertebrate brain:
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – nervous system structures that do not lie within the CNS.
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory receptors, neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception.
Glial cells, commonly called neuroglia or glia, are supportive cells that maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for the brain's neurons.
...
Wikipedia