Orotic aciduria
| Orotic aciduria | |
|---|---|
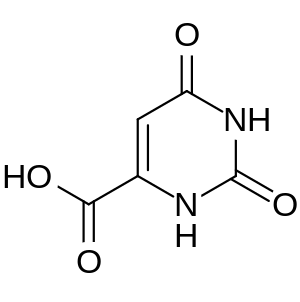 |
|
| orotic acid | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | hematology |
| ICD-10 | D53.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 281.4 |
| OMIM | 258900 258920 |
| DiseasesDB | 29294 |
Orotic aciduria is a disease yielding an excessive excretion of orotic acid in urine. It causes a characteristic form of anemia and may be associated with mental and physical retardation.
Orotic acid is an intermediate product in pyrimidine synthesis pathway, a subsequent product of which plays a role in conversion between dihydrofolate and tetrahydrofolate. Orotic aciduria is associated with megaloblastic anemia due to decreased pyrimidine synthesis, which leads to decreased nucleotide-lipid cofactors needed for erythrocyte membrane synthesis in the bone marrow.
In addition to the characteristic excessive orotic acid in the urine, patients typically have megaloblastic anemia (UMP synthase deficiency) which cannot be cured by administration of vitamin B12 or folic acid.
It also can cause inhibition of RNA and DNA synthesis and failure to thrive.
Its hereditary form, an autosomal recessive disorder, can be caused by a deficiency in the enzyme UMPS, a bifunctional protein that includes the enzyme activities of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase.
It can also arise secondary to blockage of the urea cycle, particularly in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (or OTC deficiency). This can be distinguished from hereditary orotic aciduria (seen above) by assessing blood ammonia levels and blood urea nitrogen (BUN). In OTC deficiency, hyperammonemia and decreased BUN are seen because the urea cycle is not functioning properly.
...
Wikipedia
