Operation Tumbler-Snapper
| Operation Tumbler–Snapper | |
|---|---|
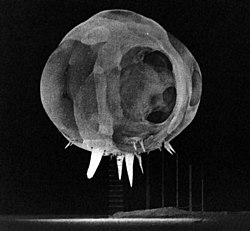
Photograph taken milliseconds after detonation of nuclear device from the "Tumbler-Snapper" test series. (The shot tower is faintly visible below fireball; downward spikes are termed "rope tricks").
|
|
| Information | |
| Country | United States |
| Test site | NTS Areas 5, 11, Frenchman Flat; NTS, Areas 1-4, 6-10, Yucca Flat |
| Period | 1952 |
| Number of tests | 8 |
| Test type | free air drop, tower |
| Max. yield | 31 kilotonnes of TNT (130 TJ) |
| Navigation | |
| Previous test series | Operation Buster–Jangle |
| Next test series | Operation Ivy |
Operation Tumbler–Snapper was a series of atomic tests conducted by the United States in early 1952 at the Nevada Test Site. The Tumbler-Snapper series of tests followed Operation Buster-Jangle, and preceded Operation Ivy.
The Tumbler phase, sponsored by the Atomic Energy Commission consisted of three airdrops which were intended to help explain discrepancies in the actual and estimated blast shock wave damage noted on previous detonations, and to establish more accurately the optimum height of burst.
The Snapper phase, sponsored by the Department of Defense consisted of one airdrop and four tower shots intended to test various new weapons developments.
The military exercise Desert Rock IV, involving 7350 soldiers, took place during the test series. They trained during the Charlie, Dog, and George shots and observed shot Fox.
...
Wikipedia
