Oncologists
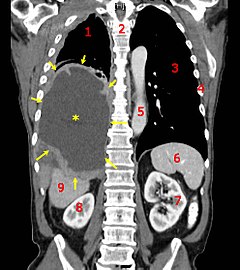
A coronal CT scan showing a malignant mesothelioma, indicated by the asterisk and the arrows
|
|
| Focus | Cancerous tumor |
|---|---|
| Subdivisions | Medical oncology, radiation oncology, surgical oncology |
| Significant tests | Tumor markers, TNM staging, CT scans, MRI |
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an oncologist. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (ónkos), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass".
The three components which have improved survival in cancer are:
Cancers are often managed through discussion on multi-disciplinary cancer conferences where medical oncologist, surgical oncologist, radiation oncologist, pathologist, radiologist and organ specific oncologists meet to find the best possible management for an individual patient considering the physical, social, psychological, emotional and financial status of the patients. It is very important for oncologists to keep updated of the latest advancements in oncology, as changes in management of cancer are quite common. All eligible patients in whom cancer progresses and for whom no standard of care treatment options are available should be enrolled in a clinical trial.
Screening is recommended for cancers of breast, cervix, colon and lung.
Symptoms usually depend on the site and type of cancer.
Diagnostic and staging investigations depend on the site and type of malignancy
Blood investigations including Haemoglobin, Total leucocyte count, Platelet count, Peripheral Smear, Red cell indices
Bone marrow studies including aspiration, Flow-cytometry, Cytogenetics, Fluorescent in situ hybridisation and molecular studies.
Excision biopsy of lymph node for Histopathological Examination (HPE), Immuno-histochemistry (IHC) and molecular studies.
Blood investigations including Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), Serum Uric Acid, Renal Functions.
Imaging tests like Computerised Tomography (CT), Positron emission tomography (PET CT).
Bone marrow biopsy.
Biopsy for histopathology & IHC.
Imaging tests like Roentgenogram (X-ray), Ultrasonography, Computerised tomography (CT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and PET CT.
Endoscopy including Naso-pharyngoscopy, Direct & Indirect Laryngoscopy, Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Colonoscopy, Cystoscopy.
tumor markers including alphafetoprotein (AFP), Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG), Carcinoembionic Antigen (CEA), CA 125, Prostate specific antigen (PSA).
Treatment depends on the site and type of cancer.
It includes Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL):
Includes acute and chronic leukemias. Acute leukemias includes acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Chronic leukemias include chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
...
Wikipedia
