Old Town (Franklin, Tennessee)
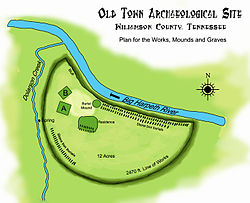
Diagram of placement of mounds and works at the Old Town Archaeological Site
|
|
| Location |
Franklin, Tennessee, Williamson County, Tennessee, |
|---|---|
| Region | Williamson County, Tennessee |
| Coordinates | 35°59′38.44″N 86°56′11.36″W / 35.9940111°N 86.9364889°W |
| History | |
| Cultures | Mississippian culture |
| Site notes | |
| Architecture | |
| Architectural styles | platform mounds, plaza |
| Architectural details | Number of temples: |
|
Old Town Archaeological Site
|
|

Old Town Archeological Site, October 2014.
|
|
| Nearest city | Franklin, Tennessee |
| Area | 41 acres (17 ha) |
| MPS | Mississippian Cultural Resources of the Central Basin MPS (40WM2) |
| NRHP Reference # | 89000159 |
| Added to NRHP | 1989 |
| Responsible body: State | |
Old Town is an archaeological site in Williamson County, Tennessee near Franklin. The site includes the remnants of a Native American village and mound complex of the Mississippian culture, and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) as Old Town Archaeological Site (40WM2).
Since the early days of settlement in Middle Tennessee, the "Old Town on the Big Harpeth River" has been a critical component of a common understanding of the area's prehistory. The earliest archaeological investigations of the site were in 1868 by physician Joseph Jones, who was then Nashville's municipal health officer; his efforts were largely frustrated because much of the site's most significant mound was occupied by the owner's wife's flower garden, but he was able to find a frog effigy from part of the mound outside the garden. W.M. Clark mentioned the location in an 1878 publication, but no more substantial excavations were conducted until 1928: while building a bridge over Brown Creek at its confluence with the river, Williamson County road crews accidentally dug into a large burial ground, and a local man worked hard to record as much information about the site as possible. Since the late twentieth century, no substantial excavations have been conducted, but the owners have permitted the recovery of artifacts from small portions of the site when construction has demanded work on the periphery; among this work has been a project to place a water pipeline in 1984 and the 1991 renovation of the Thomas Brown House on the property.
The Mississippian culture village and mound complex is located at the confluence of the Harpeth River and Dolorson Creek on the Harpeth River branch of the Natchez Trace. Archaeological investigations of the 12-acre (4.9 ha) site have uncovered artifacts dating from approximately 900 to 1450. In his book Aboriginal Remains of Tennessee, published by the Smithsonian Institution in 1876, Joseph Jones produced a detailed account of the site. The village area was surrounded by steep earthworks running in a 2,470 feet (750 m) semicircle, portions of which were topped by a wooden palisade that is interpreted as having been intended as a protective fortification. Within the enclosure, the village area includes several large earthen mounds a plaza and associated village areas. Jones described the mound grouping as including two platform mounds and two burial mounds. Mississippian mound complexes such as the Old Town complex are thought to have been regional centers for civic and ceremonial activity, as well as serving as the permanent residences of ruling elites. The mounds are located within the embankments. The largest of the rectangular platform mounds, Mound A, was 112 feet (34 m) on its longer side by 65 feet (20 m) on the shorter side and 11 feet (3.4 m) in height. The second, Mound B, was 70 feet (21 m) by 65 feet (20 m) at its base and 9 feet (2.7 m) in height. Located across a plaza area was a 30 feet (9.1 m) by 20 feet (6.1 m) in diameter 2.5 feet (0.76 m) high burial mound. The remaining burial mound is the location of the Thomas Brown House.
...
Wikipedia


