Oblique cord
| Oblique cord | |
|---|---|

Left elbow-joint, showing anterior and ulnar collateral ligaments. (Oblique cord visible as diagonal white line near center bottom.)
|
|
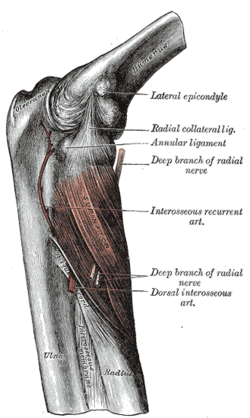
The Supinator. (Oblique cord visible at center.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | chorda obliqua membranae interosseae antebrachii |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
c_31/12236870 |
| TA | A03.5.06.003 |
| FMA | 39484 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The oblique cord is a ligament between the ulnar and radius bones in the lower arm near the elbow. It takes the form of a small, flattened band, extending downward and lateralward, from the lateral side of the ulnar tuberosity at the base of the coronoid process to the radius a little below the radial tuberosity. Its fibers run in the opposite direction to those of the Interosseous membrane of the forearm.
It is called by other names including oblique ligament, chorda obliqua, radio-ulnar ligament, chorda oblique antebrachii anterior, proximal interosseous band, dorsal oblique accessory cord, proximal band of the interosseous membrane, superior oblique ligament, oblique ligament proper, round ligament, and ligament of Weitbrecht.
It has no known function and can be cut without apparent consequence.
A study upon the arms of 38 people found that its mean length is 3.4 cm (range 2.4 to 4.2 cm) and in most people it tapers from the ulna to the radius end, being at the ulna 9 mm, in its middle, 7mm and its radius end 4 mm.
The shape and form of the ligament have been found in humans cadavers to vary from a rounded cord to a flat membrane. Further, it is not found in all humans being variably found to be absent in half of arms, and a third or 15% of people. It is found in most primates though not in the family of New World monkeys that includes spider and woolly monkeys called atelines.
It has been suggested to strengthen the interosseus membrane proximally, provide restraint for the rotatory movements of the forearm, or that the ligament may stop bone bending and preventing buckling failure. However, due the orientation of its fibers, the oblique cord is unlikely to transfer force due to limb loading from the radius to the ulna.
...
Wikipedia
