Nucleus ambiguous
| Nucleus ambiguus | |
|---|---|
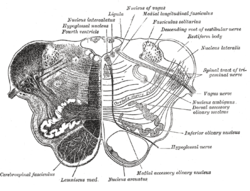
Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive. ("Nucleus ambiguus" labeled at center right.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nucleus ambiguus |
| NeuroNames | hier-762 |
| NeuroLex ID | Nucleus ambiguus |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
n_11/12580164 |
| TA | A14.1.04.253 |
| FMA | 54588 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The nucleus ambiguus (literally "ambiguous nucleus") is a group of large motor neurons, situated deep in the medullary reticular formation. The nucleus ambiguus contains the cell bodies of nerves that innervate the muscles of the soft palate, pharynx, and larynx which are strongly associated with speech and swallowing. As well as motor neurons, the nucleus ambiguus in its "external formation" contains cholinergic preganglionic parasympathetic neurons for the heart.
It is a region of histologically disparate cells located just dorsal (posterior) to the inferior olivary nucleus in the lateral portion of the upper (rostral) medulla. It receives upper motor neuron innervation directly via the corticobulbar tract.
This nucleus gives rise to the branchial efferent motor fibers of the vagus nerve (CN X) terminating in the laryngeal, pharyngeal muscles, and musculus uvulae; as well as to the efferent motor fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) terminating in the stylopharyngeus muscle.
...
Wikipedia
